According to the incomplete statistics of the Beijing News reporter, as of May 10, 65 home listed companies have released their 2019 annual reports.
In terms of revenue and net profit, enterprises in different fields are different, which can be described as mixed. The data shows that among 65 listed companies, 41 companies have achieved double growth in revenue and net profit, and 22 companies have negative growth in net profit. In addition, Yazhen Home, Yihua Life, Yongan Forestry and Dongyi Risheng suffered losses.
Among them, the competitive pressure in the home textile industry has increased; The transformation and upgrading of home stores has gradually opened up the road of new retail innovation; The growth rate of customized enterprises has slowed down, and comprehensive strength has become the key to PK; Decoration enterprises are in a difficult situation and are still exploring new online and digital modes. In addition, some wood furniture enterprises have suffered continuous losses and have implemented delisting risk warning.
Home textile industry: competitive pressure, some enterprises began to transform and upgrade.
In 2019, enterprises in the home textile industry faced greater market competition pressure, and some enterprises began to transform and upgrade. According to the statistics of the National Bureau of Statistics, from January to November 2019, the domestic output value of enterprises above designated size in China’s home textile industry reached 119.6 billion yuan, a slight increase of 0.44% year-on-year.
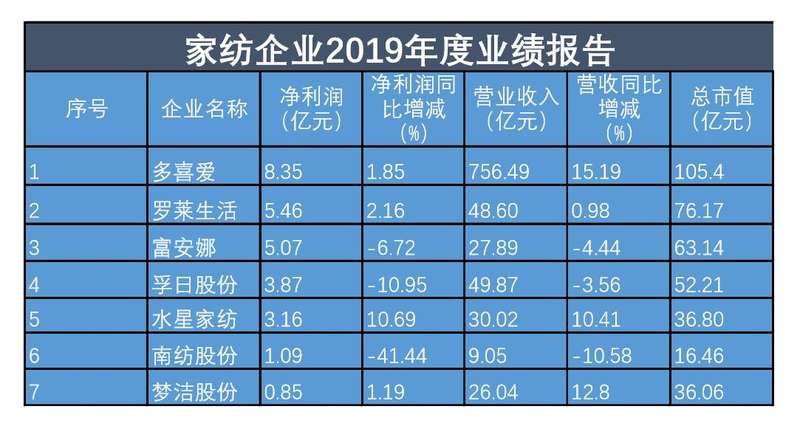
The Beijing News reporter learned that among the seven listed companies, Duoai, Luolai Life, Fuanna, Vosges, Mercury Home Textiles, Nanfang and Meng Jie, only Duoai has a total market value of over 10 billion, which is 10.54 billion yuan. Followed by Luolai Life and Fuanna, with a total market value of 7.617 billion yuan and 6.314 billion yuan respectively. Nanfang shares ranked last with 1.646 billion yuan.
The annual report shows that in 2019, the revenues and net profits of four companies, Duoai, Luolai Life, Mercury Home Textiles and Meng Jie, increased year-on-year, while the revenues and net profits of Fuanna, Vosges and Nanfang decreased year-on-year.
Among them, Duoai’s revenue in 2019 was 75.649 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 15.19%, and its net profit was 835 million yuan, a year-on-year increase of 1.85%. Both revenue and net profit ranked first. For the change of performance, I like to give two reasons. First, in December 2019, I completed the transfer registration procedures of major assets replacement, stock exchange, absorption and merger of Zhejiang Construction Investment Group Co., Ltd. and related transactions, and fulfilled the delivery obligation of the assets. Zhejiang Construction Investment Group Co., Ltd. became a holding subsidiary of the company, and its operating results were included in the scope of company merger. Second, after the reorganization, the company’s business has maintained steady development. The Beijing News reporter observed that the favorite revenue in 2018 was 903 million yuan, a year-on-year increase of 32.61%, and the net profit was 27.7848 million yuan, a year-on-year increase of 20.09%. Compared with 2018, its revenue and net profit growth slowed down significantly.
At the same time, the revenue and net profit of Luolai Life, Mercury Home Textiles and Meng Jie also increased year-on-year, with revenue of 4.86 billion yuan, 3.002 billion yuan and 2.604 billion yuan, up by 0.98%, 10.41% and 12.8% respectively. The net profit was 546 million yuan, 316 million yuan and 85 million yuan respectively, up by 2.16%, 10.69% and 119% year-on-year.
However, the revenue and net profit of Fuanna, Vosges and Nanfang declined in different degrees. Among them, Fuanna’s revenue was 2.789 billion yuan, down 4.44% year on year, and its net profit was 507 million yuan, down 6.72% year on year. Vosges’ revenue was 4.987 billion yuan, down 3.56% year-on-year, and its net profit was 387 million yuan, down 10.95% year-on-year. Nanfang’s revenue was 905 million yuan, down 10.58% year-on-year, and its net profit was 109 million yuan, down 41.44% year-on-year.
From the data point of view, the market competition pressure of home textile enterprises is greater. Compared with the data in 2018, the growth rate of revenue and net profit also dropped significantly. It is worth noting that in 2019, some home textile enterprises began to transform and upgrade, such as the transformation of Luolai Life into a one-stop brand retailer of home life, and the layout of new retail of Meng Jie shares.
Customized home: the overall growth rate slowed down, and one net profit showed negative growth for the first time.
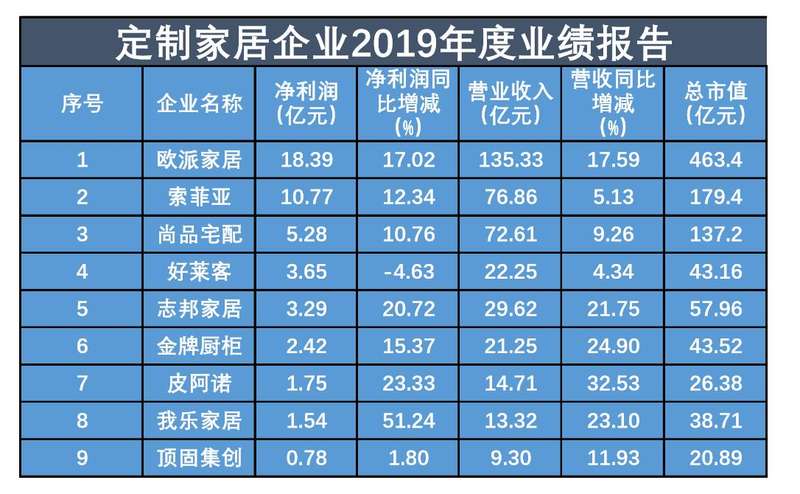
In 2019, among the nine listed customized home furnishing enterprises, three have a total market value of over 10 billion, namely Oupai Home Furnishing, Sophia and Shangpin home delivery, with a total market value of 46.34 billion yuan, 17.94 billion yuan and 13.72 billion yuan respectively. The total market value of Dinggu Jichuang, which has been listed for more than one year, is 2.089 billion yuan, ranking ninth.
The annual report shows that in 2019, nine custom-made home furnishing enterprises still maintained an upward trend, but the growth rate has obviously slowed down. According to the data, Oupai Home Furnishing, Sophia and Shangpin home delivery occupy the first place, with revenues of 13.533 billion yuan, 7.686 billion yuan and 7.261 billion yuan respectively. Oupai Home Furnishing is the only enterprise with revenues of over 10 billion yuan. The net profits of the three companies were 1.839 billion yuan, 1.077 billion yuan and 528 million yuan respectively, and the growth of revenue and net profit did not exceed 18%.
The revenue growth rates of Piano, Golden Kitchen Cabinet, Wole Home and Zhibang Home are all above 20%, with year-on-year growth figures of 32.53%, 24.90%, 23.10% and 21.75% respectively. Its net profit increased by 23.33%, 15.37%, 51.24% and 20.72% respectively.
It is worth noting that Haolaike is the only one of the nine listed companies with negative net profit growth. In 2019, its revenue was 2.225 billion yuan, up 4.34% year-on-year, and its net profit was 365 million yuan, down 4.63% year-on-year. The Beijing News reporter learned that since its listing in 2015, Haolaike’s net profit has experienced negative growth for the first time. The 2019 annual report shows that the cost investment of Haolaike has increased, and both research and development expenses and financial expenses have increased year-on-year. Haolaike said that the R&D expenses increased by 63.16% compared with the same period of last year, mainly due to the increase in company categories and increased investment in product R&D and design. The financial expenses increased by 193.94% compared with the same period of last year, mainly due to the interest expense of convertible bonds accrued during the reporting period.
From the trend of various enterprises, customized enterprises continue to develop integrated business, pursue personalization, and explore new modes of Internet and digitalization. For example, Sophia officially upgraded the brand strategy to "cabinet customization expert", and Shangpin home delivery launched the development strategy of "new model+large-scale scientific and technological infrastructure".
In 2019, the customization boom is still unabated, but the growth rate of customized home furnishing enterprises is slowly slowing down. Some industry analysts pointed out that the customized home furnishing industry has entered the second half of competition, and enterprises have made efforts in brands, channels, products and services, and the future PK is comprehensive strength.
Wood furniture: Three enterprises suffered losses and were warned of delisting risk.
In 2019, wood furniture enterprises were also happy and sad.
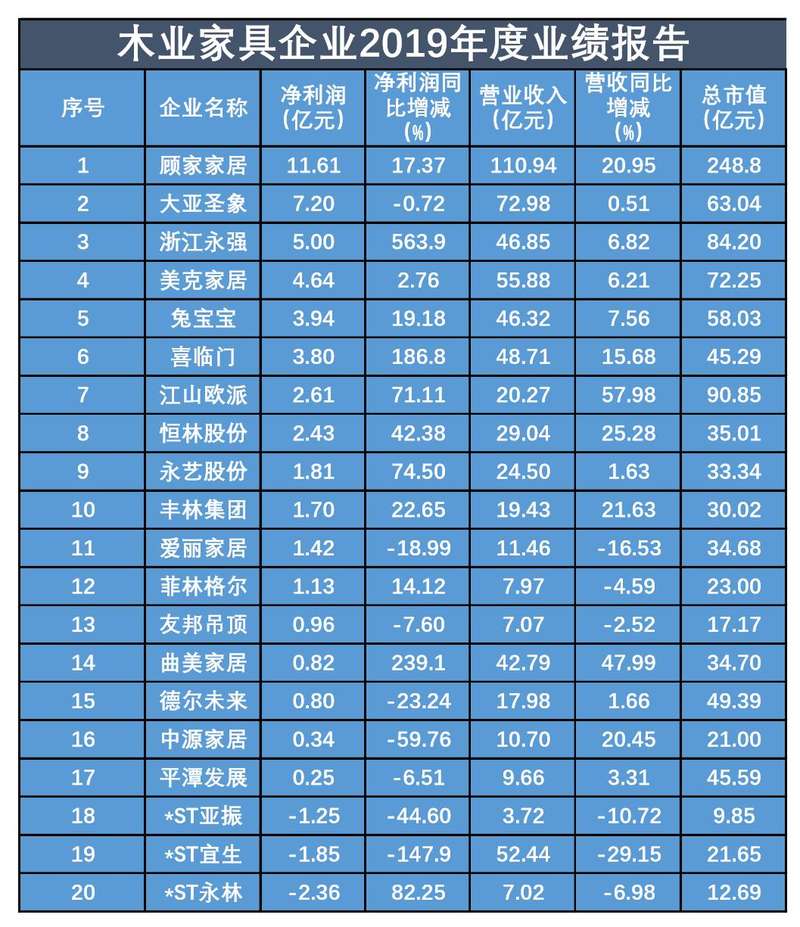
According to the incomplete statistics of the Beijing News reporter, in 2019, among the 20 listed wood furniture enterprises such as Gujia Home, Daya Icon and Qumei Home, 17 enterprises were profitable. However, three companies suffered losses and were all warned of delisting risks, namely Yazhen Home, Yihua Life and Yongan Forestry, with net profit losses of 125 million yuan, 185 million yuan and 236 million yuan respectively.
Among them, Yazhen Home has suffered a net loss for two consecutive years. From April 29, 2019, Yazhen Home implemented a delisting risk warning, and the stock abbreviation was changed to "*ST Yazhen", and it was suspended for one day on April 28, 2019. For the reason of the loss, Yazhen Home explained that due to the domestic economic environment, industry competition and household consumption classification, the revenue did not meet expectations and the overall gross profit margin declined; As well as high costs such as rent and decoration amortization, store sales are still greatly affected by the market environment, the losses of direct subsidiaries have increased, and the impairment losses of some assets have further expanded on the basis of last year.
It is worth noting that on January 5, 2020, Yazhen Home also released a plan to issue shares and pay cash to purchase assets and raise matching funds and related transactions. The plan shows that Yazhen Home will reorganize its assets and intends to purchase 100% equity of Jinmei Intelligent held by Bai Xiangfeng and Liu Youhe in total by issuing shares and paying cash. The transaction price does not exceed 1 billion yuan.
Contrary to loss-making enterprises, the net profit of Gujia Home, Daya Shengxiang and Zhejiang Yongqiang ranked in the top three, with 1.161 billion yuan, 720 million yuan and 500 million yuan respectively. Among them, Gujia Home is the only enterprise with a total market value of over 10 billion yuan, with a total market value of 24.88 billion yuan. In addition, Gujia’s home furnishing revenue was 11.094 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 20.95%, and its operating income exceeded 10 billion for the first time. According to the annual report, in 2019, Gujia Home continued to increase the number of channels, continued to enter new properties, expanded new channels such as department stores, B&Q, Suning and Shangchao, and entered more than 100 blank cities. At the same time, the "1+N+X" layout was initially realized, and the store status was fully upgraded to realize digitalization of channel management.
Home Store: "Transformation" Becomes a synonym
In 2019, "transformation" became synonymous with traditional home stores, and "big consumption" transformation, digital transformation and immersive experience emerged one after another.
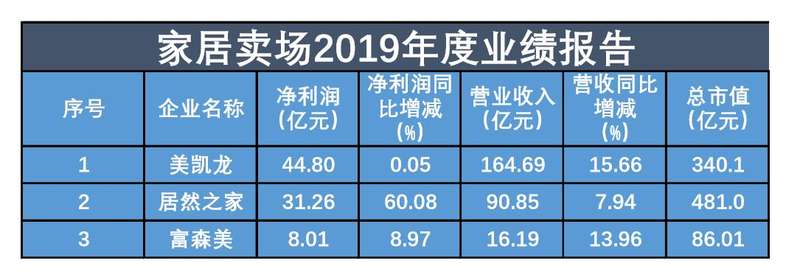
According to the annual report, in 2019, the revenues and net profits of three home stores, namely Easyhome, Red Star Macalline and Fu Sen Mei, all achieved double growth. Among them, Red Star Macalline’s revenue was 16.469 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 15.66%, and its net profit was 4.480 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 0.05%. Easyhome’s revenue was 9.085 billion yuan, up 7.94% year-on-year, and its net profit was 3.126 billion yuan, up 60.08% year-on-year. Fu Sen US revenue was 1.619 billion yuan, up 13.96% year-on-year, and net profit was 801 million yuan, up 8.97% year-on-year.
It is worth noting that Easyhome landed in A shares on December 26, 2019, and its total market value has reached 48.10 billion yuan, temporarily ranking first. The Beijing News reporter learned that since the start of strategic cooperation with Alibaba in February 2018, Real Home has started a new retail exploration journey, and continued to transform into "big consumption" in 2019, with outstanding data performance. Take double 11 as an example. In 2018, the sales of Easyhome exceeded 12 billion yuan, and in 2019, the sales of Easyhome nationwide reached 20.881 billion yuan.
Red Star Macalline is also launching new retail. Since May 2019, it has cooperated with Alibaba in many aspects. At the business level, at present, Red Star Macalline’s "Dragon Wing System" has been connected with Alibaba’s "Meow Zero POS System", further making the overall digitalization of people, goods and fields in the home furnishing industry a reality.
Household practitioners say that offline chain stores and online operations do online business in order to improve offline customer acquisition ability, and the goal of digital transformation is to make offline ecology prosper.
Decoration: Decoration enterprises explore new online and digital modes.
In 2019, it was not smooth for decoration enterprises, and "hardship" became a multi-frequency vocabulary for some home improvement entrepreneurs. According to the data of the annual report, the revenue and net profit of some enterprises also declined to varying degrees, among which one home improvement enterprise suffered losses.
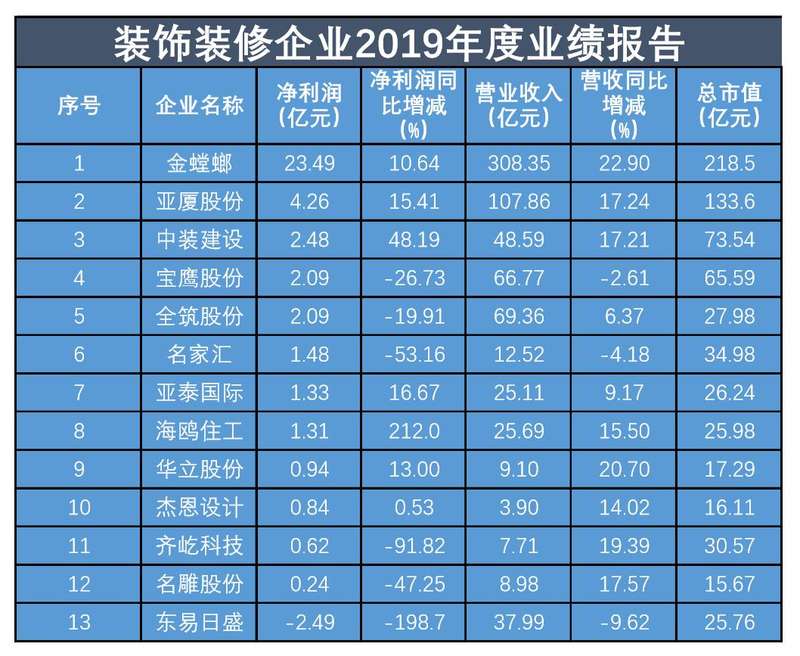
According to the incomplete statistics of the Beijing News reporter, among the 13 decoration enterprises, the total market value of Jintang and Yaxia shares exceeds 10 billion yuan, which are 21.85 billion yuan and 13.36 billion yuan respectively. At the same time, the revenue and net profit of Jintang and Yasha also ranked first and second, with revenue of 30.835 billion yuan and 10.786 billion yuan respectively, and net profit of 2.349 billion yuan and 426 million yuan respectively.
It is worth noting that Dongyi Risheng’s revenue was 3.799 billion yuan, ranking sixth among 13 decoration enterprises. However, the revenue decreased by 9.62% year-on-year. In addition, the net profit loss was 249 million yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 198.7%. Dongyi Risheng explained that the decline in revenue was mainly caused by the decline in home improvement business, while the net profit loss was mainly due to the decline in revenue and impairment of goodwill.
In addition, the revenue and net profit of some enterprises have also declined. Among them, Baoying’s revenue decreased by 2.61% and its net profit decreased by 26.73%. The revenue of Mingjiahui decreased by 4.18% and the net profit decreased by 53.16% year-on-year.
The Beijing News reporter learned that decoration companies are also exploring a new model of online and digital home improvement in 2019. In 2019, Dongyi Risheng insisted on the road of home improvement through science and technology, and used digital means to improve delivery efficiency. At the same time, Qijia. com, the main operator of Qiyi Technology, which is the representative of Internet home improvement, is also promoting the digital transformation of installation enterprises. In 2019, Qijia. com released the 2020 "Torch Upgrade Plan", which screened and supported 1,000 high-quality home improvement enterprises nationwide, and the first batch of 100 star-rated enterprises formed Qijia. com’s "Torch Library" to provide all-round support for selected enterprises, give priority to development and upgrading, and promote the home improvement industry to the Internet and digital form.
Cement building materials: the advantages of head enterprises are obvious, and the total market value of five enterprises exceeds 10 billion.
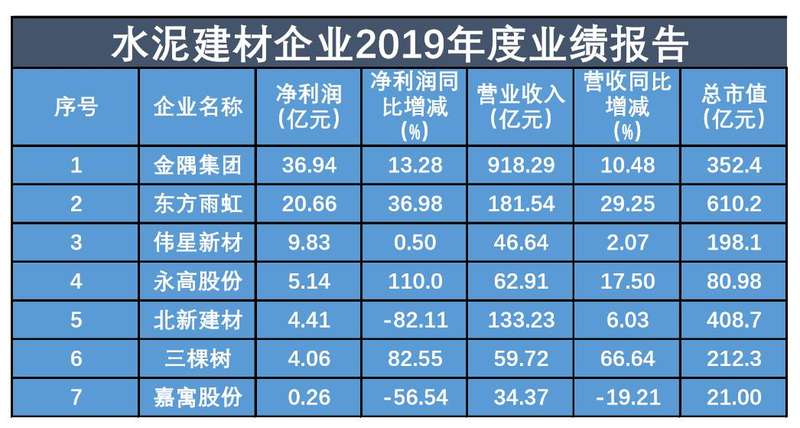
In the field of cement building materials, the Beijing News reporter learned that among the seven enterprises including Jinyu Group, Dongfang Yuhong, Sanshu and Jiayu, five enterprises have a total market value of over 10 billion yuan, namely Dongfang Yuhong 61.02 billion yuan, Beixin Building Materials 40.87 billion yuan, Jinyu Group 35.24 billion yuan, Sanshu 21.23 billion yuan and Weixing New Materials 19.81 billion yuan. Among them, Jinyu Group, Oriental Yuhong and Weixing New Materials ranked in the top three, with net profit of 3.694 billion yuan, 2.066 billion yuan and 983 million yuan respectively.
In addition, the revenue of Beixin Building Materials increased by 6.03% year-on-year, but the net profit decreased by 82.11% year-on-year. The Beijing News reporter noted that in 2019, the annual report of Beixin Building Materials mentioned that the company’s non-operating expenditure in 2019 was 2.091 billion yuan, compared with 268 million yuan in 2018, a year-on-year increase of 681.33%. In this regard, Beixin Building Materials explained that the main reason for the increase was the increase in attorney’s fees and settlement fees for plasterboard matters in the United States caused by Taishan Gypsum, a company and its secondary subsidiary. It is understood that since 2009, many homeowners and housing construction companies in the United States have filed many lawsuits against at least dozens of gypsum board manufacturers, including Beixin Building Materials and Taishan Gypsum Co., Ltd., on the grounds of gypsum board quality problems.
At the same time, the Beijing News reporter noted that the total market value of Jiayu shares was only 2.1 billion yuan, and at the same time, its revenue and net profit showed a double decline. In 2019, Jiayu’s revenue was 3.437 billion yuan, down 19.21% year-on-year, and its net profit was 26 million yuan, down 56.54% year-on-year.
The data shows that there is a big difference in revenue and net profit between cement building materials enterprises, and the head enterprise has obvious advantages, while the tail enterprise has disadvantages in competition, so it is necessary to find a breakthrough in innovation.
Bathroom industry: the competition is still fierce, and the two companies have negative growth.
In 2019, the competition in the bathroom industry is still fierce. At the same time, the whole industry still shows a trend of declining demand at the retail end and intensifying competition at the engineering end. The Beijing News reporter learned that among the six companies involved in Dior Home, Huida Sanitary Ware, Aopu Home, Songlin Technology, Ruierte and Seagull, the difference in their net profits is not great. Among them, the net profit of Dior Home ranked first with 566 million yuan, followed by Huida Sanitary Ware and Aopu Home, with net profits of 329 million yuan and 268 million yuan respectively. Seagull residents are temporarily ranked sixth with 131 million yuan.
However, in 2019, among the six enterprises, only the total market value of Dior Home exceeded 10 billion yuan, reaching 11.60 billion yuan, its revenue was 5.57 billion yuan, up 29.29% year-on-year, and its net profit was 566 million yuan, up 48.70% year-on-year. Both revenue and net profit ranked first. For the growth of performance, Dio Home explained that the synergy effect generated by its high integration with Oushennuo is remarkable, and the comprehensive competitive advantage accumulated by Oushennuo’s self-operated projects over the years has been continuously exerted. At the same time, the retail model innovation and channel sinking layout have been continuously carried out, and the overall operation of Dio Home in 2019 has achieved contrarian growth.
According to the annual report, sanitary ware and building ceramics are the two main business sectors of Dior Home. Among them, the bathroom sector is the traditional main business of the company and owns the "Emperor" bathroom brand. However, in terms of sectors, its growth is largely driven by the tile sector, and the performance of the bathroom business has shrunk.
In addition, Aopu Home and Songlin Technology experienced negative growth in revenue and net profit. Among them, Aopu Home was listed on the A-share market on January 15, 2020, with its revenue down by 2.05% and net profit down by 11.41%. The revenue of Songlin Technology decreased by 1.14% year-on-year, and the net profit decreased by 0.85% year-on-year.
It is worth noting that although the net profit of seagull residents was at the bottom of 131 million yuan, its growth rate ranked first, with a year-on-year increase of 212.03%. It explained that in 2019, we will vigorously develop the domestic sales business of our own brands, such as customized bathroom, cabinets and smart homes, and the business results of the integrated bathroom in the previous strategic layout are outstanding. From the trend of various bathroom enterprises, most enterprises are expanding the whole bathroom business.
The industry believes that with the upgrading of consumption, consumers’ requirements for quality have gradually increased, which is a good opportunity for brands with high quality. In addition, the concentration of bathroom industry is not high, even the leading brands at home and abroad still have a lot of room for development.

(Data as of May 10, 2020)
Beijing News reporter Zhang Jie
Editor Peng Yali proofreads Liu Baoqing.